About University of Port Harcourt
University of Port Harcourt
Articles by University of Port Harcourt
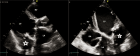
Prevalence of congenital heart diseases among primary school children in the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria, West Africa
Published on: 26th September, 2019
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8333013062
Introduction: Congenital heart diseases (CHD) are leading causes of childhood morbidity and mortality especially in developing countries. Community-based studies are important in ascertaining the burden of the disease.
Objectives: The study was set out to determine the prevalence and types of CHD among primary school children in Port Harcourt Local Government Area (PHALGA) of Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria.
Methods: A total of 1,712 primary school pupils were selected by multistage sampling from twelve schools in PHALGA. A questionnaire was used to obtain information from pupil’s parents on their child’s biodata and symptoms suggestive of heart disease. General physical and cardiovascular system examinations were carried out on each selected pupil, following which those with symptoms and/or signs suggestive of heart disease had echocardiographic confirmation of their cardiac status.
Results: The 1,712 subjects were aged 5-14 (mean 8.48 ± 2.30) years. 874 (51.1%) were females while males were 838 (48.9%). The study revealed that 31 pupils had congenital heart diseases confirmed by echocardiography, giving a prevalence of 18.1 per 1,000 pupils. The commonest cardiac defects seen were acyanotic CHD in 30 (96.8%) pupils while cyanotic CHD was seen in only one (3.2%) pupil. Among the acyanotic CHD, atrial septal defects (83.9%) followed by ventricular septal defects (9.7%) were the commonest. CHD occurred with higher frequency among females (64.5%) and among the younger age group of 5-9 years (61.3%) though these were not statistically significant (p > 0.005).
Conclusion: Cardiac examination as part of compulsory health screening at primary school entry will help detect children with CHD, reduce delay in diagnosis for intervention, avert debilitating morbidity and assure a better quality of life.
Demographic pattern of refractive anomalies in Niger Delta presbyopes - Implications for preventive eye care practice
Published on: 29th January, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8531090530
Background/Aim: In spite of global initiatives to provide sight for all by the year 2020, many middle-aged to elderly people in the Niger Delta still have significant visual impairment due to uncorrected refractive errors. The aim of this study is to assess the types of refractive anomalies that occur among presbyopic patients in Port Harcourt and determine the demographic pattern of these anomalies based on age and gender characteristics.
Methodology: This is a hospital-based descriptive cross-sectional study in which sixty consecutive adult patients for refraction were seen. Every adult patient that came to get glasses during the study period was included in the study except where ocular or systemic contraindications were present. In addition to visual acuity, all patients had a detailed ocular examination and then refraction. The collected data was subsequently analysed using SPSS version 20.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 54.4 ± 9.4 years with a range of 35 to 80 years. A total of 60 patients were seen, comprising 30 males and 30 females. The commonest refractive error was presbyopia with hyperopic astigmatism and this accounted for 80% of all cases. Hyperopic presbyopia and presbyopia alone were the least common.
Conclusion: There is a high level of cylindrical and spherical errors in Port Harcourt. The full optical correction should always be prescribed to presbyopic patients to fully correct the associated visual impairment and improve the patients’ well-being.
Socio-demographic characteristics and other factors associated with depressive illness among medical students at the University of Port Harcourt
Published on: 14th May, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8691259611
Background: The burden of depression as a mental disorder has continued to increase and constituting an enormous public health concern among all age groups. A number of socio-demographic, and other factors including a stressful and rigorous academic programme or curriculum such as the one run in most medical schools could contribute to the occurrence of depression among medical students.
AIM: To determine the socio-demographic and other factors associated with depression among medical students in the University of Port Harcourt.
Methodology: This study was a descriptive cross-sectional study. Appropriate sample size was calculated and the stratified random sampling method was used to select the subjects. A well-structured open ended self-administered socio-demographic questionnaire was administered to the students. The Zung Self-Rated Depression Scale was used to assess the depression status of each respondent. The data were analyzed via descriptive and analytical methods.
Results: The prevalence of depression among the medical students was 5.3%. Fourteen students (4.6%) were mildly depressed while only two respondents had moderate depression. Year 3 had the highest prevalence with 10.5% followed by final year with 5.3%, while the only 2 cases of moderate depression were found among students in year 2 of their medical programme. Two hundred and seventy-one respondents (88.8%) were found to have good knowledge of depression, 32 (10.5%) were found to have average knowledge of depression and 2(0.7%) had poor knowledge of depression.
Conclusion: Depression does occur among medical students at the University of Port Harcourt albeit low, and was associated with a number of socio-demographic and other factors. The present medical curriculum and programme should be sustained and more efforts at making it less stressful and academically friendly, be made to further reduce the current rate of psychological stress and depression among the students.
Risk evaluation and modeling of soils contaminated with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in parts of Bonny Island, Niger Delta, Nigeria
Published on: 27th May, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8609740211
Environmental impact of a recent oil spill incident in Bonny terminal using soil media was studied using a risk-based modeling approach. The establishment of the presence of contaminants of concern (CoC), evaluation/assessment, modeling spilled volume and ascertaining potential health risk associated with the spill incident was carried out. The Contaminant of Concern (CoC) included Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Soils and groundwater were sampled in the vicinity of the spill incident and further away into the surrounding communities. Soils were sampled into the depths (0.1 m, 0.5 m,1.0 m, 1.5 m), and the results of sieve analysis revealed that the area is predominantly silty sand in composition. This study also revealed that TPH concentration at all locations and depths exceeded DPR target value of 50 mg/kg. The TPH model revealed that a total volume of 222,500m3 of the spill area exceeded DPR intervention value of 5000 mg/kg. The results of PAH showed that only BS-1, BS-6, BS-8, BS-9 and BS-10 exceeded DPR target value of 1.0 mg/kg at some depths. All other sample depths and locations were within the target limit. The 3-D grid generated for PAH showed that 563,000m3 of the study area exceeded the DPR target value. The 3-D block models generated for TPH and PAH, along with the cross-sections and extracted time slices all showed that the concentration of the Contaminant of Concern (CoC) generally decreased with depth, and the centre of the spill located at the south-eastern part of the survey area. Based on these models, three spill zones were identified; Zone 1-highly contaminated areas (BS-8, BS-9, BS-10); Zone 2 - moderately contaminated areas (BS-1, BS-2, BS-6, BS-7); and low contaminated areas (BS-3, BS-4, BS-5). The entire soil in the area were contaminated with TPH and 47% of the area contaminated with PAH. This study has shown the effectiveness of the use of a model-based approach in quantifying hydrocarbon contamination volumes in the area. There is therefore the need for continuous monitoring of hydrocarbon spills in the area.
Toxicity and Phytochemical Analysis of Five Medicinal Plants
Published on: 25th April, 2024
Recent studies have shown that long-term uses of herbs have been associated with a rise in morbidity and mortality rates. While most researches are focused on bioactivity investigations, the toxicity of many plants has not been reported. There is a paucity of data on the potential toxicity of the following plants: Harungana madagascariensis (HM), Pterocarpus osun (PO), Phoenix dactylifera (PD), Annona muricata (AM), and Rutidea parviflora (RP). To evaluate the toxicity of the above-mentioned plants; two tests were employed namely: The Brine shrimp lethality test (BSLT) and the Allium cepa test. A correlation between the oral acute toxicity assay in mice and the LC50 obtained from BSLT has been established. Allium cepa test measures the potential genotoxic effects of plant extracts exerted on the root meristem of A. cepa (onions). Plant extracts were administered in concentrations ranging from 100 to 2500 µg/ml to the A. cepa for 72 h to obtain their Mitotic Indices (MI) and EC50. Results of the MI at 2500 µg/ml for HM, PO, PD, AM, and RP were 3.75, 4.96, 5.96, 6.10, and 6.71 while 281.81, 398.11, 501.19, 630.96, and 707.9 µg/ml were obtained as the respective EC50 values. Furthermore, 10-1000 mcg/ml concentrations were administered in the BSLT and the obtained LC50 values were 116.3, 250, 581.5, 581.5, and 750 µg/ml. The toxicity result demonstrated that the five plants were moderately toxic, with RP exhibiting minimal toxicity values and thus potentially having a good safety profile. The phytochemical screening of these plants revealed the presence of some pharmacologically important classes of compounds that are abundant. Several bioactive and toxic compounds were identified in the GC-MS analysis for some of the plants.
Male Linear Anthropometrics of Selected Nigerian Ethnicities: A Cross - Sectional Analysis
Published on: 23rd October, 2024
Introduction: This study aims at evaluating selected linear anthropometrics of three Nigerian ethnic groups to provide baseline data for the creation of 3D Negroid anatomic models.Methods: The research design was a cross-sectional design. The sampling technique was multistage proportionate random sampling. The places of study were Imo, Oyo, and Kano States of Nigeria. The study lasted for one (1) year. Random selection of 1500 adult males from three major tribes (500 Igbo, 500 Yoruba, and 500 Hausa between the ages of 18 and 40 years). Tukey’s Post Hoc test of multiple comparisons was carried out to determine the specific ethnic groups that differ in specific anthropometric parameters.Results: The differences in standing height, arm length, and thigh length across the Hausa, Igbo, and Yoruba ethnic groups are statistically significant (p < 0.05). Conclusion: The study concluded that the Igbo and Yoruba groups had higher standing heights compared to the Hausa group. Arm length was longer in the Igbo and Yoruba groups compared to the Hausa group. However, thigh length was greater in the Hausa group compared to both the Igbo and Yoruba groups, while the Hausa group had longer thigh lengths than both the Igbo and Yoruba groups. The Igbo group displayed the largest arm span, whereas the Hausa group had the widest shoulder breadth. However, the Hausa group had a lower bi-iliac breadth in comparison to the other two ethnic groups.
Adult Neurogenesis: A Review of Current Perspectives and Implications for Neuroscience Research
Published on: 12th November, 2024
Background: The study of new neuron formation in the adult brain has sparked controversy and ignited interest among scientists in recent times, these include its occurrence and location in the adult human brain, functional significance, variation in study methods, translation from animal model to human, and ethical challenges involving neural stem cell research. Aim: To provide a comprehensive understanding of adult neurogenesis, functional significance, and challenges and explore the latest advances in the study of adult neurogenesis. Methodology: An extensive and systematic search of electronic databases (Medline, Scopus, Web of Science) was conducted using keywords related to adult neurogenesis and techniques involved in its study. Results: The mechanism of adult neurogenesis was found to occur in specific brain regions such as the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus and subventricular zone of the lateral ventricle. Adult neurogenesis is vital neural plasticity, providing a potential mechanism for the brain to adapt and reorganize in response to environmental cues and experiences. Cutting-edge research and sophisticated imaging techniques, such as two-photon microscopy, MRI, optogenetic, and stem-cell-based therapies have provided deeper insight into the study of adult neurogenesis. Conclusion: The study of neurogenesis is important for understanding nervous system development, physiology, pathology, and exploring neuroplasticity. Its advancement is challenged by some ethical concerns regarding embryonic, pluripotent stem cells, and the need for safe, and noninvasive study methods. Although recent breakthroughs in neuroimaging, microscopic techniques, and genetic tools are aiding real-time study of adult neurogenesis.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."